Key Considerations When Upgrading Hospital Medical Equipment
Upgrading medical equipment is one of the most critical strategic decisions a hospital can make. Unlike routine procurement, equipment upgrades directly influence patient safety, clinical capability, operational efficiency, and long-term financial stability.
In modern healthcare environments, technology evolves rapidly while clinical expectations continue to rise. Hospitals must balance innovation with reliability, ensuring that new equipment enhances care delivery without introducing unnecessary risk or disruption.
A successful upgrade strategy requires careful evaluation beyond technical specifications, considering how equipment fits into clinical workflows, infrastructure, and future healthcare demands.
Assessing Clinical Needs and Care Objectives
The foundation of any equipment upgrade begins with a clear understanding of clinical requirements. Equipment should be selected based on patient populations, case complexity, and service lines rather than technology trends alone.
Hospitals serving high-acuity patients may prioritize advanced monitoring and life-support systems, while diagnostic centers may focus on imaging precision and throughput efficiency.
Aligning equipment upgrades with clinical objectives ensures that technology investments directly support improved patient outcomes rather than incremental functionality.

Infrastructure Compatibility and Integration
Modern medical equipment is deeply interconnected with hospital infrastructure. Power requirements, data connectivity, environmental controls, and spatial design all influence equipment performance.
Upgrading a single system without evaluating infrastructure readiness can lead to inefficiencies, downtime, or compromised performance.
Integration with existing clinical systems, electronic health records, and monitoring platforms is essential to ensure seamless data flow and coordinated care delivery.
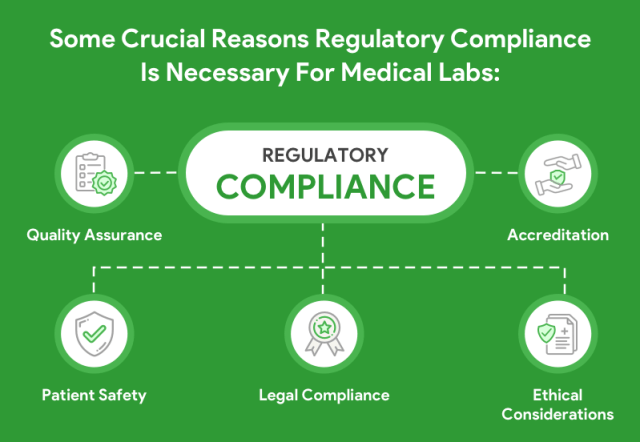
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
Medical equipment upgrades must comply with evolving regulatory standards, safety certifications, and quality assurance requirements.
Hospitals are responsible not only for procurement but also for ensuring proper installation, validation, and documentation throughout the equipment lifecycle.
Proactive risk assessment during the upgrade process reduces the likelihood of compliance issues, operational disruptions, and patient safety incidents.
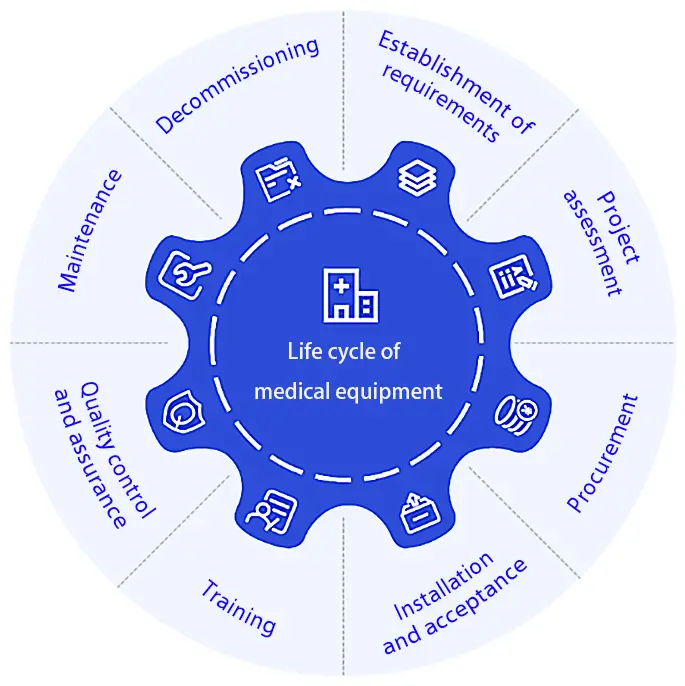
Total Cost of Ownership and Long-Term Value
Equipment acquisition costs represent only a portion of total investment. Maintenance, consumables, training, energy consumption, and system upgrades contribute significantly to long-term operational expenses.
Evaluating total cost of ownership enables hospitals to select equipment that delivers sustainable value over its entire lifespan.
Strategic upgrades prioritize durability, service support, and scalability rather than short-term savings.
Staff Training and Operational Adoption
Even the most advanced equipment cannot improve outcomes without effective clinical adoption. Training, usability, and workflow alignment are essential considerations.
Equipment interfaces should support intuitive operation, reducing cognitive load and minimizing the risk of user error in high-pressure environments.
Comprehensive training programs ensure that clinicians fully leverage equipment capabilities while maintaining confidence in daily operations.

Future Readiness and Scalability
Healthcare technology continues to evolve toward data-driven, connected, and automated care environments. Equipment upgrades must anticipate future integration and expansion.
Scalable systems allow hospitals to adopt emerging technologies without replacing entire infrastructures.
Future-ready equipment protects investment value while supporting long-term clinical innovation.
Conclusion
Upgrading hospital medical equipment is a complex, multidisciplinary decision that extends far beyond procurement.
By carefully evaluating clinical needs, infrastructure readiness, regulatory requirements, and long-term value, hospitals can implement upgrades that strengthen patient care, operational resilience, and institutional sustainability.

Leave a Reply